Electric Grid Optimization using QAOA
We have a set of N power plants (sources), and M consumers. The goal is to supply power to all consumers, meeting the constraints of the power plants, and minimize the total cost of supplying power. The presented model has small variation from [1].
Mathematical model, minimize the objective function:
where \(x_{ij}\) is the required values of the transmitted power from source \(A_i\) to consumer \(B_j\).
The unit cost of transmitting power from node \(A_i\) to node \(B_j\) is \(Z_{ij}\).
Constraint to:
The sum of powers flowing from power plant transmission lines to all customer nodes must be up to the power of the source \(A_i\)
Each consumer recieve power \(B_{j}\):
We take \(B_{j} = 1\) and \(A_{i} = 2\) in the following example.
Notice that we use 2 kinds of constraints, equality and inequality.
Building the problem
from itertools import product
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx # noqa
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
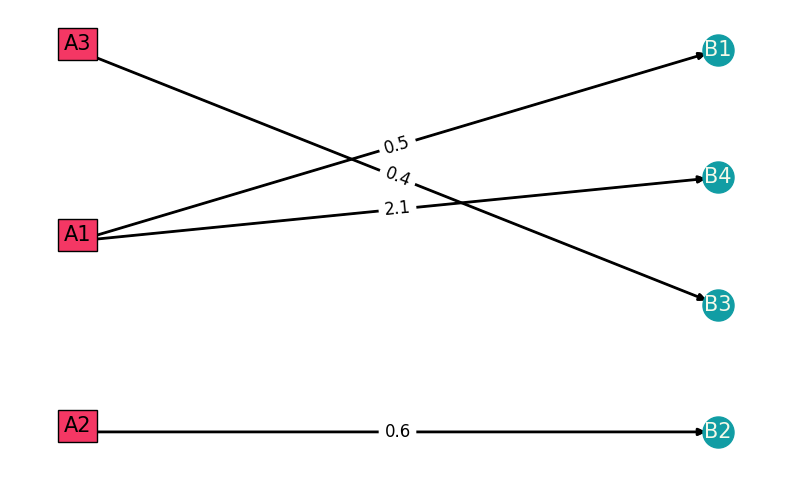
# building data matrix, it doesn't need to be a symmetric matrix.
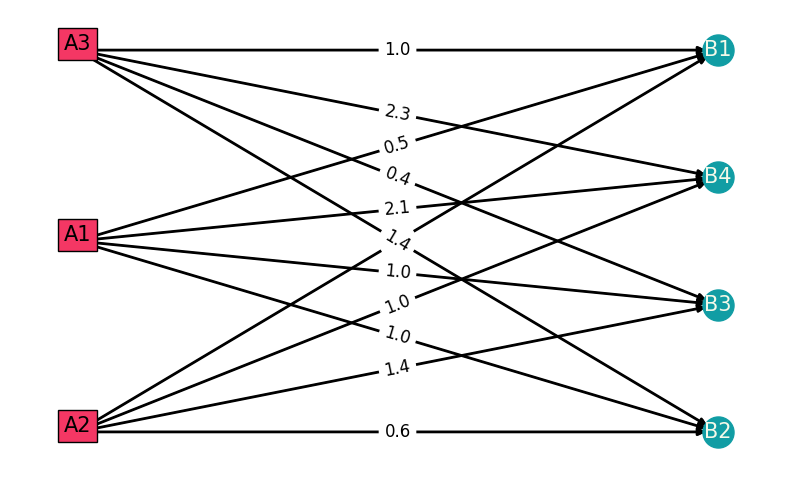
cost_matrix = np.array(
[[0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 2.1], [1.0, 0.6, 1.4, 1.0], [1.0, 1.4, 0.4, 2.3]]
)
Sources = ["A1", "A2", "A3"]
Consumers = ["B1", "B2", "B3", "B4"]
# number of sources
N = len(Sources)
# number of consumers
M = len(Consumers)
graph = nx.DiGraph()
graph.add_nodes_from(Sources + Consumers)
for n, m in product(range(N), range(M)):
graph.add_edges_from([(Sources[n], Consumers[m])], weight=cost_matrix[n, m])
# Plot the graph
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
left = nx.bipartite.sets(graph)[0]
pos = nx.bipartite_layout(graph, left)
nx.draw_networkx(graph, pos=pos, nodelist=Consumers, font_size=22, font_color="None")
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
graph, pos, nodelist=Consumers, node_color="#119DA4", node_size=500
)
for fa in Sources:
x, y = pos[fa]
plt.text(
x,
y,
s=fa,
bbox=dict(facecolor="#F43764", alpha=1),
horizontalalignment="center",
fontsize=15,
)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(graph, pos, width=2)
labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(graph, "weight")
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(graph, pos, edge_labels=labels, font_size=12)
nx.draw_networkx_labels(
graph,
pos,
labels={co: co for co in Consumers},
font_size=15,
font_color="#F4F9E9",
)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
building the pyomo model - classical combinatorial optimization problem
import pyomo.environ as pyo
from IPython.display import Markdown, display
opt_model = pyo.ConcreteModel()
sources_lst = range(N)
consumers_lst = range(M)
opt_model.x = pyo.Var(sources_lst, consumers_lst, domain=pyo.Binary)
@opt_model.Constraint(sources_lst)
def source_supply_rule(model, n): # constraint (1)
return sum(model.x[n, m] for m in consumers_lst) <= 2
@opt_model.Constraint(consumers_lst)
def each_consumer_is_supplied_rule(model, m): # constraint (2)
return sum(model.x[n, m] for n in sources_lst) == 1
opt_model.cost = pyo.Objective(
expr=sum(
cost_matrix[n, m] * opt_model.x[n, m]
for n in sources_lst
for m in consumers_lst
),
sense=pyo.minimize,
)
Printing the classical optimization problem
opt_model.pprint()
5 Set Declarations
each_consumer_is_supplied_rule_index : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 4 : {0, 1, 2, 3}
source_supply_rule_index : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 3 : {0, 1, 2}
x_index : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=True
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 2 : x_index_0*x_index_1 : 12 : {(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3)}
x_index_0 : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 3 : {0, 1, 2}
x_index_1 : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 4 : {0, 1, 2, 3}
1 Var Declarations
x : Size=12, Index=x_index
Key : Lower : Value : Upper : Fixed : Stale : Domain
(0, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
1 Objective Declarations
cost : Size=1, Index=None, Active=True
Key : Active : Sense : Expression
None : True : minimize : 0.5*x[0,0] + x[0,1] + x[0,2] + 2.1*x[0,3] + x[1,0] + 0.6*x[1,1] + 1.4*x[1,2] + x[1,3] + x[2,0] + 1.4*x[2,1] + 0.4*x[2,2] + 2.3*x[2,3]
2 Constraint Declarations
each_consumer_is_supplied_rule : Size=4, Index=each_consumer_is_supplied_rule_index, Active=True
Key : Lower : Body : Upper : Active
0 : 1.0 : x[0,0] + x[1,0] + x[2,0] : 1.0 : True
1 : 1.0 : x[0,1] + x[1,1] + x[2,1] : 1.0 : True
2 : 1.0 : x[0,2] + x[1,2] + x[2,2] : 1.0 : True
3 : 1.0 : x[0,3] + x[1,3] + x[2,3] : 1.0 : True
source_supply_rule : Size=3, Index=source_supply_rule_index, Active=True
Key : Lower : Body : Upper : Active
0 : -Inf : x[0,0] + x[0,1] + x[0,2] + x[0,3] : 2.0 : True
1 : -Inf : x[1,0] + x[1,1] + x[1,2] + x[1,3] : 2.0 : True
2 : -Inf : x[2,0] + x[2,1] + x[2,2] + x[2,3] : 2.0 : True
9 Declarations: x_index_0 x_index_1 x_index x source_supply_rule_index source_supply_rule each_consumer_is_supplied_rule_index each_consumer_is_supplied_rule cost
Solving with Classiq
We take a specific example: the one outlined above.
First generating parameters for the quantum circuit
from classiq import *
from classiq.applications.combinatorial_optimization import CombinatorialProblem
combi = CombinatorialProblem(pyo_model=opt_model, num_layers=4, penalty_factor=10)
qmod = combi.get_model()
write_qmod(qmod, "electric_grid_optimization")
Synthesizing the QAOA Circuit and Solving the Problem
We can now synthesize and view the QAOA circuit (ansatz) used to solve the optimization problem:
qprog = combi.get_qprog()
show(qprog)
Opening: https://platform.classiq.io/circuit/2uoG3GJW6emTBf8T50yNWlssqIh?login=True&version=0.73.0
We now solve the problem by calling the optimize method of the CombinatorialProblem object. For the classical optimization part of the QAOA algorithm we define the maximum number of classical iterations (maxiter) and the \(\alpha\)-parameter (quantile) for running CVaR-QAOA, an improved variation of the QAOA algorithm [3]:
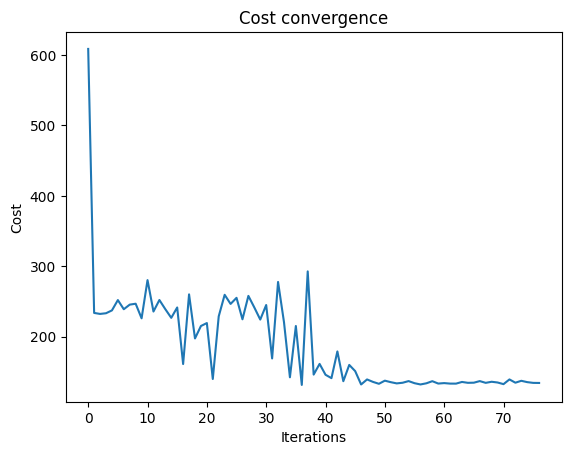
optimized_params = combi.optimize(maxiter=100, quantile=1)
Optimization Progress: 77%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▉ | 77/100 [06:49<02:02, 5.32s/it]
We can check the convergence of the run:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(combi.cost_trace)
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Cost")
plt.title("Cost convergence")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Cost convergence')
Get best solution statistics
optimization_result = combi.sample(optimized_params)
optimization_result.sort_values(by="cost").head(5)
| solution | probability | cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 628 | {'x': [[0, 0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0... | 0.000488 | 4.9 |
| 1141 | {'x': [[1, 0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1... | 0.000488 | 5.2 |
| 1591 | {'x': [[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1... | 0.000488 | 5.6 |
| 1273 | {'x': [[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1... | 0.000488 | 23.2 |
| 1448 | {'x': [[0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1... | 0.000488 | 23.7 |
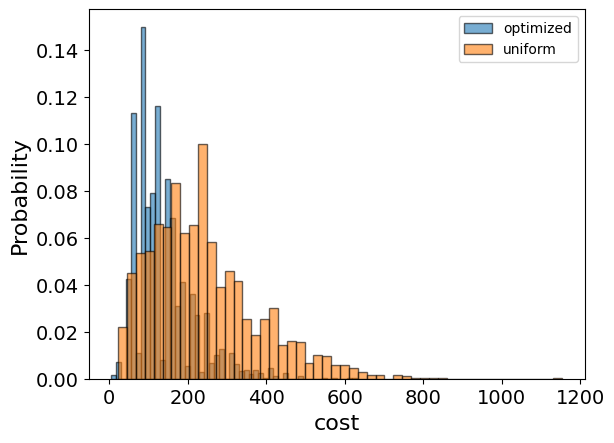
We also want to compare the optimized results to uniformly sampled results:
uniform_result = combi.sample_uniform()
And compare the histograms:
optimization_result["cost"].plot(
kind="hist",
bins=50,
edgecolor="black",
weights=optimization_result["probability"],
alpha=0.6,
label="optimized",
)
uniform_result["cost"].plot(
kind="hist",
bins=50,
edgecolor="black",
weights=uniform_result["probability"],
alpha=0.6,
label="uniform",
)
plt.legend()
plt.ylabel("Probability", fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel("cost", fontsize=16)
plt.tick_params(axis="both", labelsize=14)
Best solution visulalization
# This function plots the solution in a table and a graph
def plotting_sol(x_sol, cost, is_classic: bool):
x_sol_to_mat = np.reshape(np.array(x_sol), [N, M]) # vector to matrix
# opened facilities will be marked in red
opened_fac_dict = {}
for fa in range(N):
if sum(x_sol_to_mat[fa, m] for m in range(M)) > 0:
opened_fac_dict.update({Sources[fa]: "background-color: #F43764"})
# classical or quantum
if is_classic == True:
display(Markdown("**CLASSICAL SOLUTION**"))
print("total cost= ", cost)
else:
display(Markdown("**QAOA SOLUTION**"))
print("total cost= ", cost)
# plotting in a table
df = pd.DataFrame(x_sol_to_mat)
df.columns = Consumers
df.index = Sources
plotable = df.style.apply(lambda x: x.index.map(opened_fac_dict))
display(plotable)
# plotting in a graph
graph_sol = nx.DiGraph()
graph_sol.add_nodes_from(Sources + Consumers)
for n, m in product(range(N), range(M)):
if x_sol_to_mat[n, m] > 0:
graph_sol.add_edges_from(
[(Sources[n], Consumers[m])], weight=cost_matrix[n, m]
)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
left = nx.bipartite.sets(graph_sol, top_nodes=Sources)[0]
pos = nx.bipartite_layout(graph_sol, left)
nx.draw_networkx(
graph_sol, pos=pos, nodelist=Consumers, font_size=22, font_color="None"
)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
graph_sol, pos, nodelist=Consumers, node_color="#119DA4", node_size=500
)
for fa in Sources:
x, y = pos[fa]
if fa in opened_fac_dict.keys():
plt.text(
x,
y,
s=fa,
bbox=dict(facecolor="#F43764", alpha=1),
horizontalalignment="center",
fontsize=15,
)
else:
plt.text(
x,
y,
s=fa,
bbox=dict(facecolor="#F4F9E9", alpha=1),
horizontalalignment="center",
fontsize=15,
)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(graph_sol, pos, width=2)
labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(graph_sol, "weight")
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(graph, pos, edge_labels=labels, font_size=12)
nx.draw_networkx_labels(
graph_sol,
pos,
labels={co: co for co in Consumers},
font_size=15,
font_color="#F4F9E9",
)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
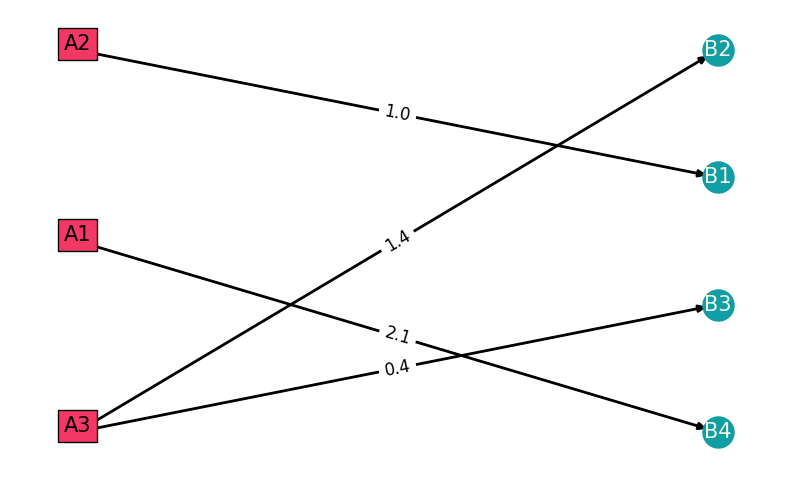
best_solution = optimization_result.loc[optimization_result.cost.idxmin()]
plotting_sol(
[best_solution.solution["x"][i] for i in range(len(best_solution.solution["x"]))],
best_solution.cost,
is_classic=False,
)
QAOA SOLUTION
total cost= 4.9
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Compare to a classical solver
from pyomo.opt import SolverFactory
solver = SolverFactory("couenne")
solver.solve(opt_model)
best_classical_solution = np.array(
[pyo.value(opt_model.x[idx]) for idx in np.ndindex(cost_matrix.shape)]
).reshape(cost_matrix.shape)
plotting_sol(
np.round([pyo.value(opt_model.x[idx]) for idx in np.ndindex(cost_matrix.shape)]),
pyo.value(opt_model.cost),
is_classic=True,
)
CLASSICAL SOLUTION
total cost= 2.4999999996418167
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| A2 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 |
| A3 | 0.000000 | -0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 |
[1]: Solving optimization problems when designing power supply circuits. https://www.e3s-conferences.org/articles/e3sconf/pdf/2019/50/e3sconf_ses18_04011.pdf