Min Graph Coloring Problem
Background
Given a graph \(G = (V,E)\), find the minimal number of colors k required to properly color it. A coloring is legal if:
-
each vetrex \({v_i}\) is assigned with a color \(k_i \in \{0, 1, ..., k-1\}\)
-
adajecnt vertex have different colors: for each \(v_i, v_j\) such that \((v_i, v_j) \in E\), \(k_i \neq k_j\). A graph which is k-colorable but not (k−1)-colorable is said to have chromatic number k. The maximum bound on the chromatic number is \(D_G + 1\), where \(D_G\) is the maximum vertex degree. The graph coloring problem is known to be in the NP-hard complexity class.
Solving the problem with classiq
Define the optimization problem
We encode the graph coloring with a matrix of variables X with dimensions \(k \times |V|\) using one-hot encoding, such that a \(X_{ki} = 1\) means that vertex i is colored by color k.
We require that each vertex is colored by exactly one color and that 2 adjacent vertices have different colors.
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
import pyomo.environ as pyo
def define_min_graph_coloring_model(graph, max_num_colors):
model = pyo.ConcreteModel()
nodes = list(graph.nodes())
colors = range(0, max_num_colors)
model.x = pyo.Var(colors, nodes, domain=pyo.Binary)
x_variables = np.array(list(model.x.values()))
adjacency_matrix = nx.convert_matrix.to_numpy_array(graph, nonedge=0)
adjacency_matrix_block_diagonal = np.kron(np.eye(degree_max), adjacency_matrix)
model.conflicting_color_constraint = pyo.Constraint(
expr=x_variables @ adjacency_matrix_block_diagonal @ x_variables == 0
)
@model.Constraint(nodes)
def each_vertex_is_colored(model, node):
return sum(model.x[color, node] for color in colors) == 1
def is_color_used(color):
is_color_not_used = np.prod([(1 - model.x[color, node]) for node in nodes])
return 1 - is_color_not_used
# minimize the number of colors in use
model.value = pyo.Objective(
expr=sum(is_color_used(color) for color in colors), sense=pyo.minimize
)
return model
Initialize the model with example graph
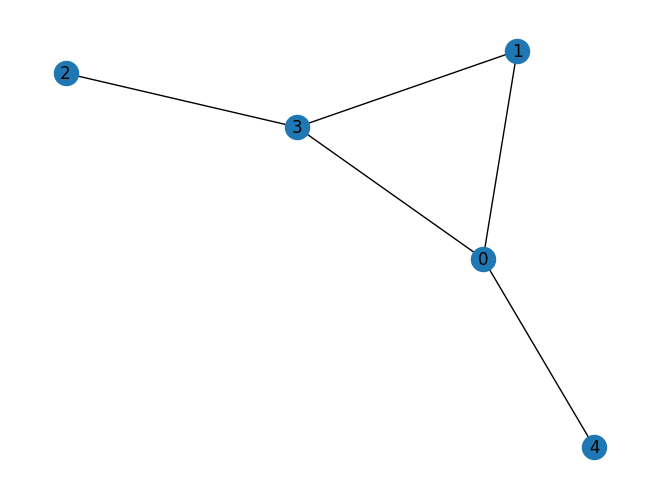
graph = nx.erdos_renyi_graph(5, 0.3, seed=79)
nx.draw_kamada_kawai(graph, with_labels=True)
degree_sequence = sorted((d for n, d in graph.degree()), reverse=True)
degree_max = max(degree_sequence)
max_num_colors = degree_max
coloring_model = define_min_graph_coloring_model(graph, max_num_colors)
show the resulting pyomo model
coloring_model.pprint()
4 Set Declarations
each_vertex_is_colored_index : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 5 : {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
x_index : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=True
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 2 : x_index_0*x_index_1 : 15 : {(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (0, 4), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4)}
x_index_0 : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 3 : {0, 1, 2}
x_index_1 : Size=1, Index=None, Ordered=Insertion
Key : Dimen : Domain : Size : Members
None : 1 : Any : 5 : {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
1 Var Declarations
x : Size=15, Index=x_index
Key : Lower : Value : Upper : Fixed : Stale : Domain
(0, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
1 Objective Declarations
value : Size=1, Index=None, Active=True
Key : Active : Sense : Expression
None : True : minimize : 1 - (1 - x[0,0])*(1 - x[0,1])*(1 - x[0,2])*(1 - x[0,3])*(1 - x[0,4]) + 1 - (1 - x[1,0])*(1 - x[1,1])*(1 - x[1,2])*(1 - x[1,3])*(1 - x[1,4]) + 1 - (1 - x[2,0])*(1 - x[2,1])*(1 - x[2,2])*(1 - x[2,3])*(1 - x[2,4])
2 Constraint Declarations
conflicting_color_constraint : Size=1, Index=None, Active=True
Key : Lower : Body : Upper : Active
None : 0.0 : (x[0,1] + x[0,3] + x[0,4])*x[0,0] + (x[0,0] + x[0,3])*x[0,1] + x[0,3]*x[0,2] + (x[0,0] + x[0,1] + x[0,2])*x[0,3] + x[0,0]*x[0,4] + (x[1,1] + x[1,3] + x[1,4])*x[1,0] + (x[1,0] + x[1,3])*x[1,1] + x[1,3]*x[1,2] + (x[1,0] + x[1,1] + x[1,2])*x[1,3] + x[1,0]*x[1,4] + (x[2,1] + x[2,3] + x[2,4])*x[2,0] + (x[2,0] + x[2,3])*x[2,1] + x[2,3]*x[2,2] + (x[2,0] + x[2,1] + x[2,2])*x[2,3] + x[2,0]*x[2,4] : 0.0 : True
each_vertex_is_colored : Size=5, Index=each_vertex_is_colored_index, Active=True
Key : Lower : Body : Upper : Active
0 : 1.0 : x[0,0] + x[1,0] + x[2,0] : 1.0 : True
1 : 1.0 : x[0,1] + x[1,1] + x[2,1] : 1.0 : True
2 : 1.0 : x[0,2] + x[1,2] + x[2,2] : 1.0 : True
3 : 1.0 : x[0,3] + x[1,3] + x[2,3] : 1.0 : True
4 : 1.0 : x[0,4] + x[1,4] + x[2,4] : 1.0 : True
8 Declarations: x_index_0 x_index_1 x_index x conflicting_color_constraint each_vertex_is_colored_index each_vertex_is_colored value
Initialize classiq QAOA solver
Setting Up the Classiq Problem Instance
In order to solve the Pyomo model defined above, we use the Classiq combinatorial optimization engine. For the quantum part of the QAOA algorithm (QAOAConfig) - define the number of repetitions (num_layers):
from classiq import *
from classiq.applications.combinatorial_optimization import OptimizerConfig, QAOAConfig
qaoa_config = QAOAConfig(num_layers=6, penalty_energy=10.0)
For the classical optimization part of the QAOA algorithm we define the maximum number of classical iterations (max_iteration) and the \(\alpha\)-parameter (alpha_cvar) for running CVaR-QAOA, an improved variation of the QAOA algorithm [3]:
optimizer_config = OptimizerConfig(alpha_cvar=0.3)
Lastly, we load the model, based on the problem and algorithm parameters, which we can use to solve the problem:
qmod = construct_combinatorial_optimization_model(
pyo_model=coloring_model,
qaoa_config=qaoa_config,
optimizer_config=optimizer_config,
)
We also set the quantum backend we want to execute on:
from classiq.execution import ClassiqBackendPreferences
qmod = set_execution_preferences(
qmod, backend_preferences=ClassiqBackendPreferences(backend_name="simulator")
)
write_qmod(qmod, "min_graph_coloring")
Synthesizing the QAOA Circuit and Solving the Problem
We can now synthesize and view the QAOA circuit (ansatz) used to solve the optimization problem:
qprog = synthesize(qmod)
show(qprog)
Opening: https://platform.classiq.io/circuit/8da93adf-8ec5-44a4-838a-7d1f172c55db?version=0.41.0.dev39%2B79c8fd0855
We now solve the problem by calling the execute function on the quantum program we have generated:
result = execute(qprog).result_value()
We can check the convergence of the run:
result.convergence_graph
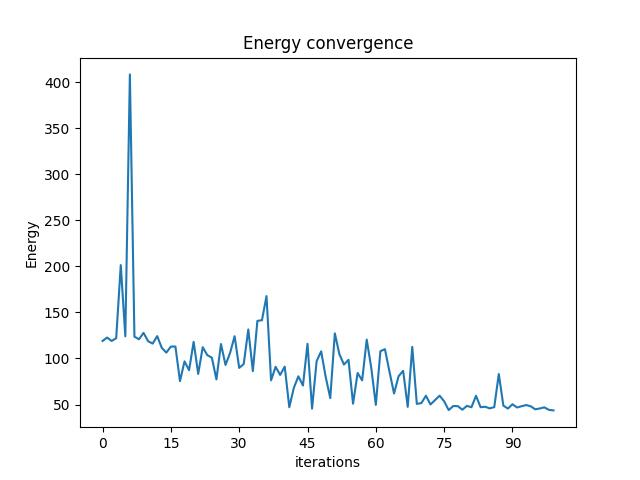
Optimization Results
We can also examine the statistics of the algorithm:
import pandas as pd
from classiq.applications.combinatorial_optimization import (
get_optimization_solution_from_pyo,
)
solution = get_optimization_solution_from_pyo(
coloring_model, vqe_result=result, penalty_energy=qaoa_config.penalty_energy
)
optimization_result = pd.DataFrame.from_records(solution)
optimization_result.sort_values(by="cost", ascending=True).head(5)
| probability | cost | solution | count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 301 | 0.001 | 3.0 | [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] | 1 |
| 466 | 0.001 | 3.0 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0] | 1 |
| 734 | 0.001 | 12.0 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1] | 1 |
| 47 | 0.002 | 12.0 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1] | 2 |
| 533 | 0.001 | 12.0 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] | 1 |
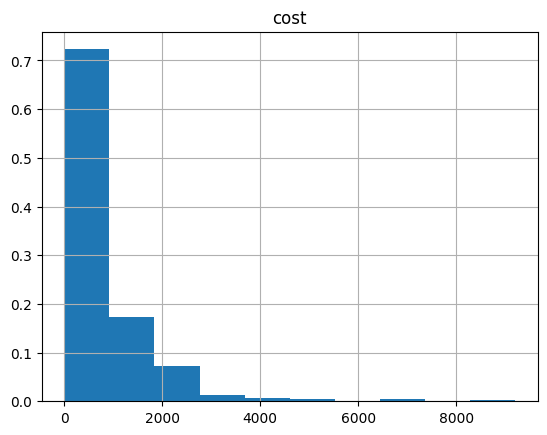
And the histogram:
optimization_result.hist("cost", weights=optimization_result["probability"])
array([[<Axes: title={'center': 'cost'}>]], dtype=object)
Let us plot the best solution:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
best_solution = optimization_result.solution[optimization_result.cost.idxmin()]
one_hot_solution = np.array(best_solution).reshape([max_num_colors, len(graph.nodes)])
integer_solution = np.argmax(one_hot_solution, axis=0)
nx.draw_kamada_kawai(
graph, with_labels=True, node_color=integer_solution, cmap=plt.cm.rainbow
)
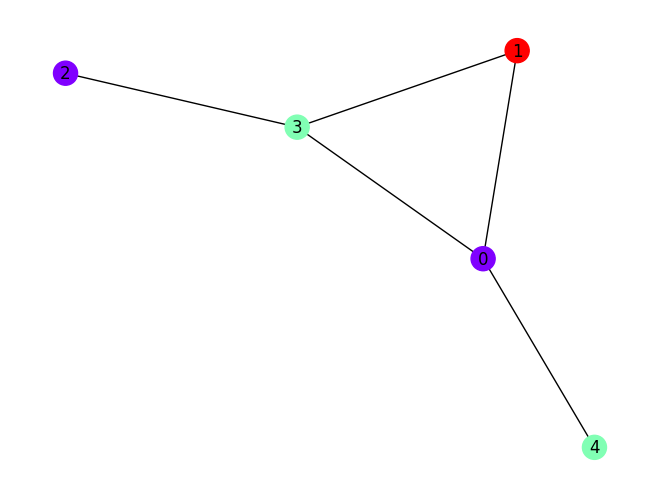
Classical optimizer results
Lastly, we can compare to the classical solution of the problem:
from pyomo.common.errors import ApplicationError
from pyomo.opt import SolverFactory
solver = SolverFactory("couenne")
result = None
try:
result = solver.solve(coloring_model)
except ApplicationError:
print("Solver might have not exited normally. Try again")
coloring_model.display()
ERROR: Solver (asl) returned non-zero return code (-11)
ERROR: Solver log: Couenne 0.5.8 -- an Open-Source solver for Mixed Integer
Nonlinear Optimization Mailing list: couenne@list.coin-or.org
Instructions: http://www.coin-or.org/Couenne couenne:
Solver might have not exited normally. Try again
Model unknown
Variables:
x : Size=15, Index=x_index
Key : Lower : Value : Upper : Fixed : Stale : Domain
(0, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(0, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(1, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 0) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 1) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 2) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 3) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
(2, 4) : 0 : None : 1 : False : True : Binary
Objectives:
value : Size=1, Index=None, Active=True
ERROR: evaluating object as numeric value: x[0,0]
(object: <class 'pyomo.core.base.var._GeneralVarData'>)
No value for uninitialized NumericValue object x[0,0]
ERROR: evaluating object as numeric value: value
(object: <class 'pyomo.core.base.objective.ScalarObjective'>)
No value for uninitialized NumericValue object x[0,0]
Key : Active : Value
None : None : None
Constraints:
conflicting_color_constraint : Size=1
Key : Lower : Body : Upper
None : 0.0 : None : 0.0
each_vertex_is_colored : Size=5
Key : Lower : Body : Upper
0 : 1.0 : None : 1.0
1 : 1.0 : None : 1.0
2 : 1.0 : None : 1.0
3 : 1.0 : None : 1.0
4 : 1.0 : None : 1.0
if result:
classical_solution = [
pyo.value(coloring_model.x[i, j])
for i in range(max_num_colors)
for j in range(len(graph.nodes))
]
one_hot_solution = np.array(classical_solution).reshape(
[max_num_colors, len(graph.nodes)]
)
integer_solution = np.argmax(one_hot_solution, axis=0)
nx.draw_kamada_kawai(
graph, with_labels=True, node_color=integer_solution, cmap=plt.cm.rainbow
)