Hamiltonian Evolution for a Water Molecule
This tutorial demonstrates the ability of the Classiq synthesis engine to reduce depth and cx-counts in approximated quantum functions for Hamiltonian evolution, focusing on Suzuki-Trotter (ST) and qDRIFT (qD) product formulas and their controlled operations. In addition, it is compared to the equivalent quantum examples in Qiskit.
The demonstration is for the Hamiltonian of a water molecule, which has 551 terms and a dimension of 12 qubits.
Define a molecule and get the Hamiltonian as a list of Pauli strings and coefficients:
from classiq.applications.chemistry import Molecule, MoleculeProblem
molecule_H2O = Molecule(
atoms=[("O", (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)), ("H", (0, 0.586, 0.757)), ("H", (0, 0.586, -0.757))]
)
gs_problem = MoleculeProblem(
molecule=molecule_H2O,
basis="sto3g",
mapping="jordan_wigner",
z2_symmetries=False,
freeze_core=True,
)
pauli_list = gs_problem.generate_hamiltonian().pauli_list
Transfer the Hamiltonian to the relevant structure in Classiq:
from typing import cast
from classiq import Pauli, PauliTerm
my_list = {"I": Pauli.I, "X": Pauli.X, "Y": Pauli.Y, "Z": Pauli.Z}
def pauli_str_to_enums(pauli):
return [my_list[s] for s in pauli]
def pauli_list_to_hamiltonian(pauli_list):
return [
PauliTerm(
pauli=pauli_str_to_enums(pauli), coefficient=cast(complex, coeff).real
)
for pauli, coeff in pauli_list
]
hamiltonian = pauli_list_to_hamiltonian(pauli_list)
These cases are examined:
ORDERS_for_ST = [1, 2, 4]
REPETITIONS_for_ST = [6, 4, 1]
N_QDS_for_qDRIFT = [1000, 2000]
classiq_depths = []
classiq_cx_counts = []
# transpilation_options = {"classiq": "custom", "qiskit": 3}
transpilation_options = {"classiq": "auto optimize", "qiskit": 1}
1. Approximating with Suzuki-Trotter formulas
from classiq import (
CustomHardwareSettings,
Preferences,
QArray,
QuantumProgram,
allocate,
create_model,
qfunc,
set_preferences,
suzuki_trotter,
synthesize,
)
preferences = Preferences(
custom_hardware_settings=CustomHardwareSettings(basis_gates=["cx", "u"]),
transpilation_option=transpilation_options["classiq"],
)
all_qprogs = []
for k in range(len(ORDERS_for_ST)):
@qfunc
def main() -> None:
qbv = QArray("qbv")
allocate(len(pauli_list[0][0]), qbv)
suzuki_trotter(
pauli_operator=hamiltonian,
evolution_coefficient=1,
order=ORDERS_for_ST[k],
repetitions=REPETITIONS_for_ST[k],
qbv=qbv,
)
qmod = create_model(main)
qmod = set_preferences(qmod, preferences=preferences)
qprog = synthesize(qmod)
all_qprogs.append(qprog)
classiq_depths.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.depth)
classiq_cx_counts.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.count_ops["cx"])
2. Implementing Controlled Hamiltonian Dynamics
from classiq import QBit, control
for k in range(2):
@qfunc
def main() -> None:
qbv = QArray("qbv")
allocate(len(pauli_list[0][0]), qbv)
ctrl = QBit("ctrl")
allocate(1, ctrl)
control(
ctrl=ctrl,
stmt_block=lambda: suzuki_trotter(
pauli_operator=hamiltonian,
evolution_coefficient=1,
order=ORDERS_for_ST[k],
repetitions=REPETITIONS_for_ST[k],
qbv=qbv,
),
)
qmod = create_model(main)
qmod = set_preferences(qmod, preferences=preferences)
qprog = synthesize(qmod)
all_qprogs.append(qprog)
classiq_depths.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.depth)
classiq_cx_counts.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.count_ops["cx"])
3. Approximating with the qDRIFT Formula
from classiq import qdrift
for n_qd in N_QDS_for_qDRIFT:
@qfunc
def main() -> None:
qbv = QArray("qbv")
allocate(len(pauli_list[0][0]), qbv)
qdrift(
pauli_operator=hamiltonian,
evolution_coefficient=1,
num_qdrift=n_qd,
qbv=qbv,
)
qmod = create_model(main)
qmod = set_preferences(qmod, preferences=preferences)
qprog = synthesize(qmod)
all_qprogs.append(qprog)
classiq_depths.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.depth)
classiq_cx_counts.append(qprog.transpiled_circuit.count_ops["cx"])
4. Comparing to Qiskit Implementation
Comments:
-
Qiskit's Suzuki-Trotter of order 1 is a separate function, called the Lie-Trotter function.
-
Qiskit's qDRIFT takes a long time to run for unclear problems. Alternatively, a random product formula is implemented, which is equivalent to qDRIFT.
The qiskit data was generated using qiskit version 1.0.0. To run the qiskit code uncomment the commented cells below.
qiskit_cx_counts = [25164, 33508, 41882, 186067, 248232, 3581, 7404]
qiskit_depths = [30627, 42879, 53581, 300924, 402125, 3463, 7141]
# from importlib.metadata import version
# try:
# import qiskit
# if version('qiskit') != "1.0.0":
# !pip uninstall qiskit -y
# !pip install qiskit==1.0.0
# except ImportError:
# !pip install qiskit==1.0.0
# from qiskit.circuit.library import PauliEvolutionGate
# from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
# from qiskit.synthesis import LieTrotter as LieTrotter_qiskit
# qiskit_depths = []
# qiskit_cx_counts = []
# operator = SparsePauliOp.from_list(pauli_list)
# gate = PauliEvolutionGate(operator, 1)
# ## Suzuki-Trotter of order 1 = Lie-Trotter
# from qiskit import transpile
# lt = LieTrotter_qiskit(reps=REPETITIONS_for_ST[0])
# circ = lt.synthesize(gate)
# tqc = transpile(
# circ, basis_gates=["u", "cx"], optimization_level=transpilation_options["qiskit"]
# )
# qiskit_depths.append(tqc.depth())
# qiskit_cx_counts.append(tqc.count_ops()["cx"])
# ## Suzuki-Trotter
# from qiskit.synthesis import SuzukiTrotter as SuzukiTrotter_qiskit
# for k in range(1, 3):
# st = SuzukiTrotter_qiskit(order=ORDERS_for_ST[k], reps=REPETITIONS_for_ST[k])
# circ = st.synthesize(gate)
# tqc = transpile(
# circ,
# basis_gates=["u", "cx"],
# optimization_level=transpilation_options["qiskit"],
# )
# qiskit_depths.append(tqc.depth())
# qiskit_cx_counts.append(tqc.count_ops()["cx"])
# # Controlled dynamics
# lt_ctrl = LieTrotter_qiskit(reps=REPETITIONS_for_ST[0])
# circ = lt_ctrl.synthesize(gate).control(1)
# tqc = transpile(
# circ, basis_gates=["u", "cx"], optimization_level=transpilation_options["qiskit"]
# )
# qiskit_depths.append(tqc.depth())
# qiskit_cx_counts.append(tqc.count_ops()["cx"])
# for k in range(1, 2):
# st_ctrl = SuzukiTrotter_qiskit(order=ORDERS_for_ST[k], reps=REPETITIONS_for_ST[k])
# circ = st_ctrl.synthesize(gate).control(1)
# tqc = transpile(
# circ,
# basis_gates=["u", "cx"],
# optimization_level=transpilation_options["qiskit"],
# )
# qiskit_depths.append(tqc.depth())
# qiskit_cx_counts.append(tqc.count_ops()["cx"])
# ## For qDRIFT, generate a random sequence
# import numpy as np
# def index_channel(n, list_coe):
# """
# This function gets an ordered list of coefficients 'list_coe' and a number of calls 'n' as inputs.
# It returns a random ordered list of size n with elements from list_coe',
# where the probability of choosing the i-th elements is list_coe[i]/sum(list_coe),
# """
# coe = np.array(list_coe) / sum(list_coe)
# c_coe = np.cumsum(coe)
# return np.searchsorted(c_coe, np.random.uniform(size=n))
# assert (
# pauli_list[0][0] == len(pauli_list[0][0]) * "I"
# ), """The Identity term is not the first on the list of Paulis,
# please modify the code accordingly """
# pauli_list_without_id = pauli_list[1::]
# po_coe = [
# np.abs(np.real(p[1])) for p in pauli_list_without_id
# ] # gets absolute value of coefficients
# for n_qd in N_QDS_for_qDRIFT:
# new_indices = index_channel(n_qd, po_coe)
# small_lambda = sum(po_coe)
# randomly_generated_pauli_list = [
# (
# pauli_list_without_id[new_indices[k]][0],
# np.sign(pauli_list_without_id[new_indices[k]][1]) * small_lambda / n_qd,
# )
# for k in range(n_qd)
# ]
# randomly_generated_pauli_list += [pauli_list[0]] # adding the identity
# gate_qd = PauliEvolutionGate(
# SparsePauliOp.from_list(randomly_generated_pauli_list), 1
# )
# qd = LieTrotter_qiskit(reps=1)
# circ = qd.synthesize(gate_qd)
# tqc = transpile(
# circ,
# basis_gates=["u", "cx"],
# optimization_level=transpilation_options["qiskit"],
# )
# qiskit_depths.append(tqc.depth())
# qiskit_cx_counts.append(tqc.count_ops()["cx"])
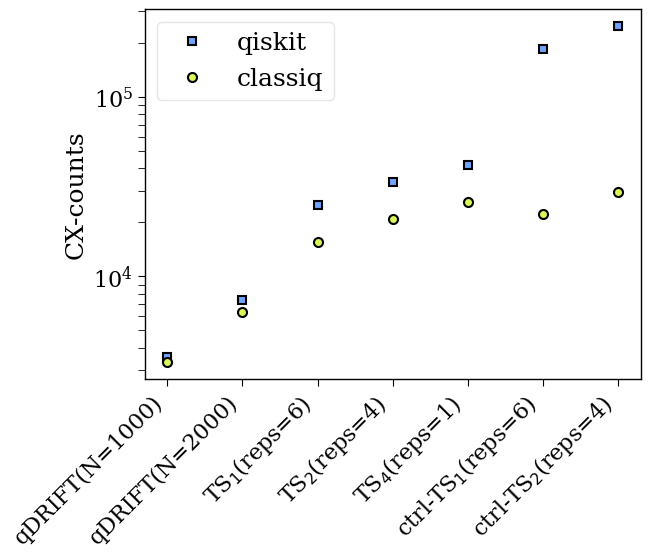
5. Plotting the Data
print("The cx-counts on Classiq:", classiq_cx_counts)
print("The cx-counts on Qiskit:", qiskit_cx_counts)
The cx-counts on Classiq: [15588, 20798, 25992, 22188, 29598, 3330, 6330]
The cx-counts on Qiskit: [25164, 33508, 41882, 186067, 248232, 3581, 7404]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
classiq_color = "#D7F75B"
qiskit_color = "#6FA4FF"
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "serif"
plt.rc("savefig", dpi=300)
plt.rcParams["axes.linewidth"] = 1
plt.rcParams["xtick.major.size"] = 5
plt.rcParams["xtick.minor.size"] = 5
plt.rcParams["ytick.major.size"] = 5
plt.rcParams["ytick.minor.size"] = 5
plt.semilogy(
qiskit_cx_counts[-2::] + qiskit_cx_counts[0:5],
"s",
label="qiskit",
markerfacecolor=qiskit_color,
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=6,
markeredgewidth=1.5,
)
plt.semilogy(
classiq_cx_counts[-2::] + classiq_cx_counts[0:5],
"o",
label="classiq",
markerfacecolor=classiq_color,
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=6.5,
markeredgewidth=1.5,
)
labels = [
"qDRIFT(N=1000)",
"qDRIFT(N=2000)",
"TS$_1$(reps=6)",
"TS$_2$(reps=4)",
"TS$_4$(reps=1)",
"ctrl-TS$_1$(reps=6)",
"ctrl-TS$_2$(reps=4)",
]
plt.xticks([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], labels, rotation=45, fontsize=16, ha="right")
plt.ylabel("CX-counts", fontsize=18)
plt.yticks(fontsize=16)
plt.legend(loc="upper left", fontsize=18, fancybox=True, framealpha=0.5)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f165654b210>